TOKYO

A novel and relatively pain-less treatment method for male urethral stricture using patients own buccal mucosal cells has been reported as successful in four out of six patients. The study has been published in International Journal of Urology (https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/iju.13852) which is the official journal of Japanese Urological Association, is a result of collaboration between Japanese biomaterial technology and an Indian urologist Dr Suryaprakash Vaddi.
This press release features multimedia. View the full release here: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20181125005123/en/
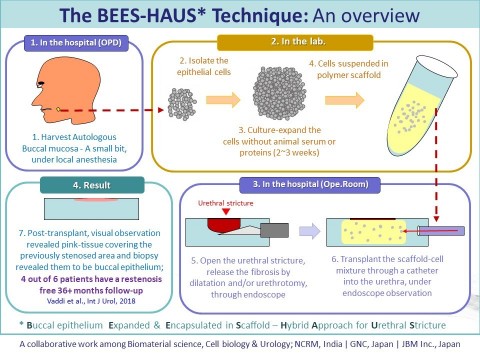
BEES-HAUS, an illustrative overview of the steps from tissue harvest to cell transplant for urethral stricture and a glimpse of the results (Graphic: Business Wire)
Majority of male urethral strictures reported in the developed world are due to iatrogenic causes (BPH surgery, prostate cancer treatment). In the developing countries, the major causes are inflammation and trauma. In 30% patients, the cause is unknown. The conventional treatment involves either endoscopic intervention or open surgery. In surgical treatment, under general anesthesia, patient’s Buccal mucosa is harvested and used as a patch to enlarge the narrowed urethra. In both methods, restenosis occurs in up to 40% of patients. In our method called as BEES-HAUS (Buccal epithelium Expanded and Encapsulated in Scaffold – Hybrid Approach for Urethral Stricture), we harvested a small piece of the buccal tissue and after culturing the cells in the lab without animal protein, embedded in scaffold and transplanted through endoscopy. Both harvesting and transplant doesn’t require general anesthesia, making the procedure relatively easier to the clinician and less painful to the patient. Going by the data, this procedure has a potential to help approximately 30,000 patients every year in Japan. In the U.S, total annual expenditure due to stricture is about 200 Million US Dollars, said Dr Vaddi, the lead author of the paper.
GN Corporation, which has coordinated the interaction between Japanese biomaterial scientists and clinicians in India through NCRM (Nichi-In Centre for Regenerative Medicine), has applied for a patent for this invention and has signed a MoU for collaboration with JBM Inc (www.jbmed.net), Tokyo, Japan, for exploring opportunities to make this an approved clinical solution in the future following the regulatory protocols as per Japanese ministry of health.
View source version on businesswire.com: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20181125005123/en/
CONTACT
Samuel JK Abraham
info@gncorporation.com