TOKYO

Heartseed Inc. (CEO: Keiichi Fukuda) today announced that it has entered into a worldwide non-exclusive patent license agreement (“Agreement”) with an undisclosed biotech company (“Licensee”) for its Metabolic Selection technology, a proprietary platform used to selectively remove undifferentiated induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs).
This press release features multimedia. View the full release here: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20230905227225/en/
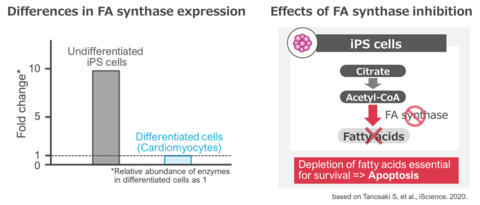
Fatty Acid (FA) synthase expression and the effect of its inhibition (Graphic: Business Wire)
This technology addresses the need to eliminate potentially tumor-causing undifferentiated iPSCs as the clinical use of iPSC-based cell therapies advances.
Covered Patent: Patent No. JP6811489(B) and foreign patent applications*1
The Licensee, which specializes in manufacturing mesenchymal stem cells from iPSCs for various diseases, aims to enhance regenerative medicine development by efficiently eliminating undifferentiated iPSCs using Heartseed’s technology.
Under the terms of the Agreement, Heartseed grants the Licensee a non-exclusive license with sublicensing rights, in exchange for an upfront payment and royalties on covered product sales. Specific financial terms and the licensee’s identity remain undisclosed.
Heartseed’s Metabolic Selection technology focuses on purifying cardiomyocytes from iPSCs for cardiac regenerative medicine. Developed in collaboration with the Division of Cardiology at Keio University School of Medicine, this technology efficiently removes undifferentiated iPSCs and non-cardiomyocytes through tailored energy metabolism and culture medium composition adjustments. It includes methods such as fatty acid synthesis inhibition, lactate, and glutamine methods, all known for selectively obtaining cardiomyocytes.
The fatty acid synthesis inhibition method covered by the agreement simplifies the removal of undifferentiated iPSCs for clinical applications, making it suitable for large-scale production. This method targets the higher expression of fatty acid synthase in undifferentiated iPSCs compared to differentiated cardiomyocytes, selectively inducing cell death in the former. The effect on differentiated cardiomyocytes is limited, and cell death does not occur. Furthermore, this method has the potential for use in other cell types beyond cardiomyocytes, such as neurons and liver cells. Heartseed intends to expand licensing to companies interested in utilizing our Metabolic Selection patents for various applications, not limited to cardiac regenerative medicine.
*1 Heartseed has obtained the exclusive license from Keio University
For details: https://www.heartseed.jp/en/index.html
View source version on businesswire.com: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20230905227225/en/
CONTACT
Kikuo Yasui
COO, Heartseed Inc.
Tel: +81-3-6380-1068
Email: kikuo.yasui@heartseed.jp